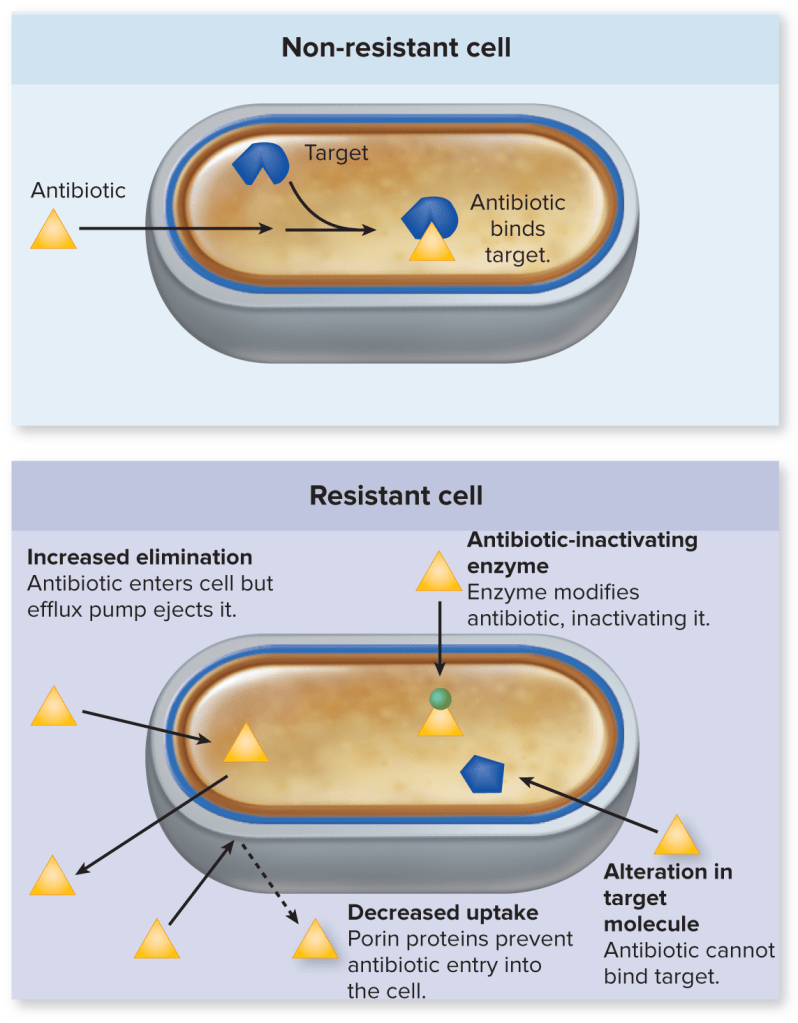
Microorganisms are continually evolving, which allows pathogens to develop resistance to certain available antimicrobial medications and because of this scientists are constantly creating new versions. According to Brinda and her colleagues, there are multiple mechanisms of acquired resistance which include antibiotic-inactivating enzymes, alteration in the target molecule, increased elimination of the medication, and decreased uptake of the medication. Through these mechanisms, the prevalence of antibiotic resistant organisms is steadily rising and individuals around the world are alarmed because of the implications that could follow including impacts on the cost, complications, and outcomes of treatment.
Campylobacter species are a common cause of food-borne diarrhea and they have been found to be resistant to ciprofloxacin and azithromycin. As a zoonotic pathogen, Campylobacter has a broad animal reservoir and infects humans via contaminated food, water or milk. The concern regarding the resistance of Campylobacter species is growing and Elhadidy and his colleagues sought to characterize the antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni recovered from diarrheal patients, focusing on the underlying molecular mechanisms and genetic diversity of resistant strains. These researchers claim that “an increase in the resistance of Campylobacter to antibiotics has been reported worldwide. In addition, recent studies have also revealed that patients infected with antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter species suffer a longer duration of diarrhea when compared with those who are infected with antimicrobial-susceptible strains”. They concluded that Campylobacter jejuni acquires resistance through mutation and horizontal gene transfer and the appearance of these resistant strains is a significant public health threat. Investigations into the mechanisms and implications of Campylobacter resistance will persist due to the number of unknown factors that come into play at the microbial level.
According to our textbook, many organisms are developing resistance to antimicrobials and the situation has become so severe that the CDC published a document titled Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. This document lists the most serious threats and categorizes them by level (urgent, serious, or concerning). Many factors that come into play when discussing the prevention of antibiotic resistance and many of them involve the responsibilities of physicians and their patients. Patients are instructed to carefully follow the instructions that accompany their prescriptions which includes taking the correct dose and completing the entire prescribed course of treatment. It is just as important for physicians to increase their efforts to identify the cause of infection to correctly prescribe the correct antimicrobial medication. Again, the prevention of antibiotic resistance is complicated and complex but research into specific resistant species and strains will continue to be conducted until we are able to hopefully one day eradicate microbes’ ability to become resistant.